Hop on board – the fashion train is speeding up. Because of the internet, hyperconnected users and their devices are driving consumer expectations faster than ever. This has created an urgency for brands and entrepreneurs to improve fashion manufacturing and quickly collect user data, sales performance, customer feedback, and supply chain issues.
1. Even More Sophisticated Machinery
Advanced algorithms are transforming the way the fashion manufacturing industry collects information, performs skilled labor, and records consumer behavior. Some even predict themes in trending patterns, silhouettes, colors, and styles. Large manufacturers are partnering with large computer companies to develop and perfect Artificial Intelligence Systems to do these tasks, and more.

2. Shortening Lead Times

‘Impatience’ has become the societal norm, so shortening lead times is key to delivery with optimum timing. Large and small companies are taking steps for the entire process to be “in-house” to increase speed and supply chain efficiency. Things like materials sourcing, creative and technical design, samples, production, and shipping are under the same roof.
3. Fashion on Demand
New technologies like automation and data analytics are shifting consumer expectations. Many brands are switching to made-to-order production cycles. The result is a reduced level of overstock and less clothing that ends in landfills. There seems also to an increase in small-batch production cycles. In this ecology-minded vein, Parisian brand Dressarte offers 100% customized sustainable clothing. New York-based software company ShareCloth contributes to the on-demand brand by digitizing styles. They create 3D samples of garments and 3D virtual bodies of the customers enabling retailers to place orders before manufacturing the products.
On-demand production requires lower capital investment which leads to a small batch inventory and to a more sustainable production cycle. However, due to the lower quantities of garments produced the manufacturing costs are higher.

4. Robots & Factories

Advancements in robotics have equipped robots with memory and agility making them highly programmable and collaborative. Just two years ago robotics startup Sewbo launched a robot capable of sewing a t-shirt without any human intervention using water-soluble stiffening solutions to turn cloth into cardboard-like material to enable robotic manufacturing.
5. Digitizing Production
Factories of the future will be completely automated with self-repairing and self-servicing structures. Requiring minimal human intervention. They will allow predictive analytics and self-diagnostics. With the help of real-time processing and data analysis, fully integrated smart factories will provide a highly accurate overview of all stages of the manufacturing process.
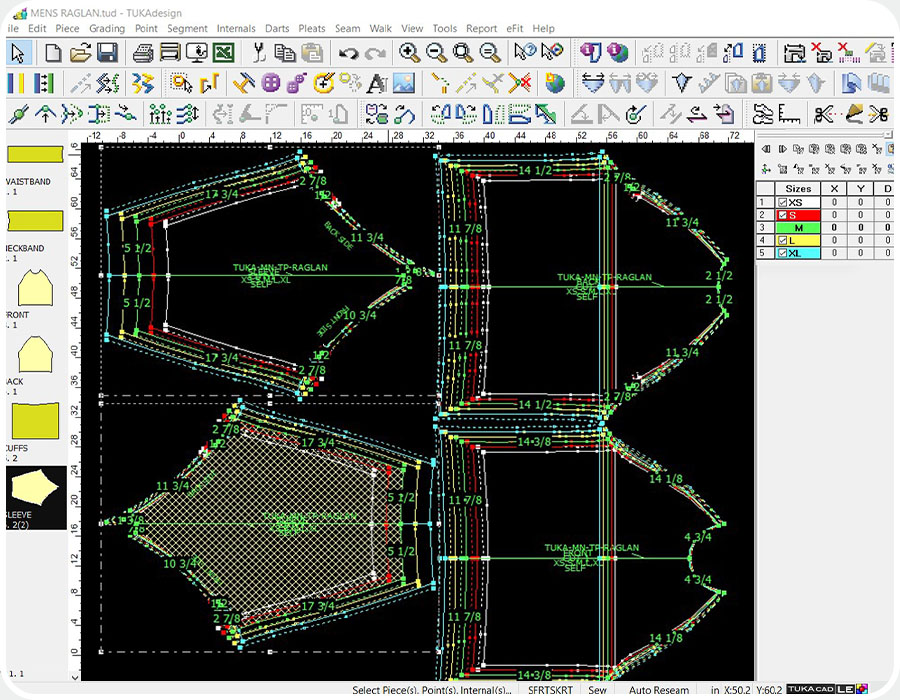
6. 3D Design & Printing
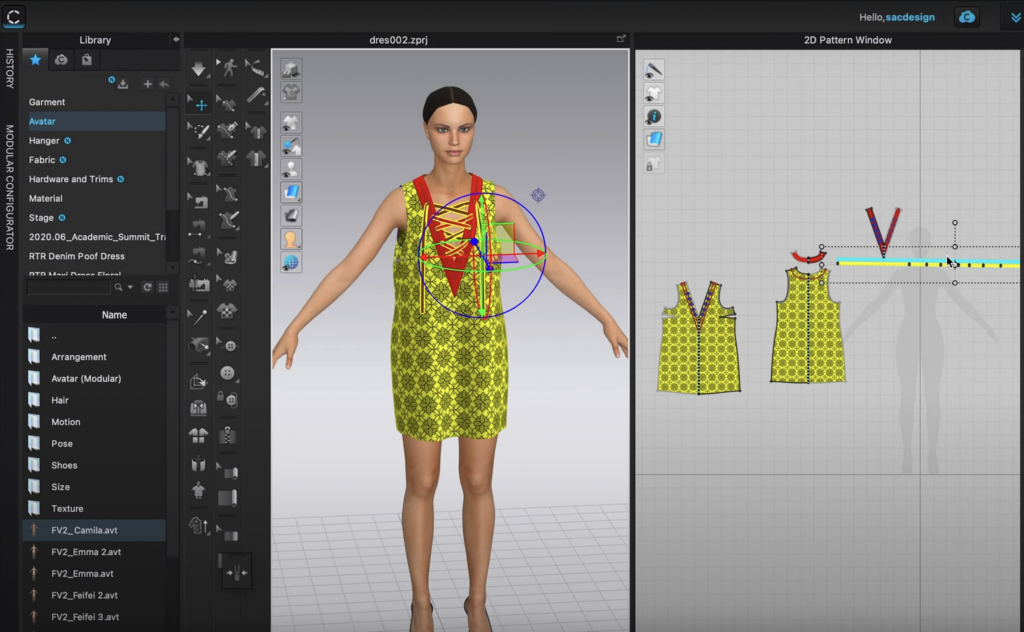
Brands are exploring how 3D printing can help them produce goods on-demand and create new avenues for customization. There are new 3D rendering technologies which allow brands to edit designs at the moment and instantly review changes. Also, 3D printing has been huge for on-demand production. Apparel brand Ministry of Supply uses an in-store 3D printer to create customized knitwear on the spot. Australia-based fashion label Shima Seiki, can turn cones of yarn into a full, seamless garment in less than one hour.
